什么是 URL Scheme?
简单回顾一下 URL Scheme 的概念。
URL Scheme 是一种自定义的 URL 前缀,格式为 scheme://host/path?query#fragment,它允许你的应用注册一个或多个 Scheme,当用户点击一个带有该 Scheme 的链接时,系统会尝试打开能够处理这个 Scheme 的应用。
一个完整的 URL 结构分解:
scheme://host/path?query#fragmentscheme(协议): 必须的,是你的应用的唯一标识符,通常使用你的应用名称或反向域名。myapp、twitter、fb。host(主机): 可选的,用来进一步标识你想要打开应用中的哪个部分。path(路径): 可选的,通常用来传递一些标识符,比如用户 ID、商品 ID 等。query(查询): 可选的,这是传递参数最常见的方式,格式为key=value,多个参数用&分隔。fragment(片段): 可选的,通常用于在已打开的页面内定位到某个特定元素,或者传递一些简单的标识。
如何定义和传递参数?
参数主要通过 Query 和 Path 两种方式传递。
通过 Query (查询字符串) 传递参数
这是最常用、最灵活的方式,适用于传递多个键值对参数。
URL 示例:
myapp://product/detail?productId=12345&source=push_notification
scheme:myapphost:productpath:detailquery:productId=12345&source=push_notificationproductId是键,12345是值。source是键,push_notification是值。- 两个参数用
&连接。
通过 Path (路径) 传递参数
这种方式通常用于表示一种层级关系或传递一个核心的、唯一的标识符。
URL 示例 1 (单个 ID):
myapp://user/98765
scheme:myapphost: (无)path:user/98765(这里的98765就是一个参数)
URL 示例 2 (多级路径):
myapp://store/category/electronics/item/67890
scheme:myapppath**:store/category/electronics/item/67890`这种方式清晰地表达了导航的层级结构。
如何在 iOS 中处理这些参数?
处理 URL 参数主要分为两个步骤:
- 在 Info.plist 中注册 URL Scheme。
- 在
AppDelegate或SceneDelegate中解析 URL。
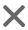
步骤 1: 注册 URL Scheme
在 Xcode 中,打开你的项目,选择 TARGETS -> Info 标签页,找到 URL Types,点击 添加一个新的 URL Type。
- URL Schemes: 输入你的 Scheme 名称(
myapp),这里可以输入多个,用逗号隔开。 - URL Identifier: 输入一个唯一的反向域名标识符(
com.yourcompany.myapp),这个是必须的,用于区分不同的应用。
步骤 2: 解析和处理 URL
当用户点击你的 Scheme 链接时,系统会调用你的应用的代理方法。
对于 iOS 13 及以上 (使用 SceneDelegate):
// SceneDelegate.swift
import UIKit
class SceneDelegate: UIResponder, UIWindowSceneDelegate {
func scene(_ scene: UIScene, openURLContexts URLContexts: Set<UIOpenURLContext>) {
// 1. 获取被打开的 URL
guard let url = URLContexts.first?.url else { return }
// 2. 解析 URL
handleDeepLink(url: url)
}
func handleDeepLink(url: URL) {
// 3. 检查 Scheme 是否匹配
guard url.scheme == "myapp" else { return }
// 4. 解析 Query 参数
if let queryItems = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: true)?.queryItems {
for item in queryItems {
if let value = item.value {
print("Query Param: \(item.name) = \(value)")
}
}
}
// 5. 解析 Path
let pathComponents = url.pathComponents
print("Path Components: \(pathComponents)")
// 示例: 处理 myapp://user/98765
if pathComponents.count == 2 && pathComponents[1] == "user" {
if let userId = pathComponents.last {
print("Navigating to user profile with ID: \(userId)")
// 在这里执行跳转到用户详情页面的逻辑
}
}
// 示例: 处理 myapp://product/detail?productId=12345
if pathComponents.contains("product") && pathComponents.contains("detail") {
if let productId = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: true)?.queryItems?.first(where: { $0.name == "productId" })?.value {
print("Navigating to product detail with ID: \(productId)")
// 在这里执行跳转到商品详情页面的逻辑
}
}
}
}
对于 iOS 13 以下 (使用 AppDelegate):
// AppDelegate.swift
import UIKit
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
func application(_ app: UIApplication, open url: URL, options: [UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey : Any] = [:]) -> Bool {
// 1. 解析 URL
handleDeepLink(url: url)
return true
}
func handleDeepLink(url: URL) {
// ... 解析逻辑与 SceneDelegate 中完全相同 ...
// (复制上面的 handleDeepLink 函数体即可)
}
}
高级用法和最佳实践
参数编码
URL 中有些字符(如空格、&、、)是特殊字符,如果直接用在参数值中会导致 URL 解析错误,在生成 URL 时,必须对参数进行编码。
- Objective-C: 使用
[str stringByAddingPercentEncodingWithAllowedCharacters:] - Swift: 使用
str.addingPercentEncoding(withAllowedCharacters:)
示例 (Swift):
let source = "App Store & News" let encodedSource = source.addingPercentEncoding(withAllowedCharacters: .urlQueryAllowed)! let urlString = "myapp://link?source=\(encodedSource)" print(urlString) // 输出: myapp://link?source=App%20Store%20%26%20News
使用 URLComponents 进行构建和解析
为了更安全、更方便地处理 URL,推荐使用 URLComponents。
构建一个复杂的 URL (Swift):
var components = URLComponents()
components.scheme = "myapp"
components.host = "order"
components.path = "/confirm"
// 添加查询参数
components.queryItems = [
URLQueryItem(name: "orderId", value: "order-xyz-123"),
URLQueryItem(name: "discount", value: "20%"),
URLQueryItem(name: "referral", value: "friend_code_abc")
]
if let url = components.url {
print(url.absoluteString) // 输出: myapp://order/confirm?orderId=order-xyz-123&discount=20%25&referral=friend_code_abc
// 注意:百分号 % 也会被编码为 %25
}
解析一个 URL (Swift):
let urlString = "myapp://order/confirm?orderId=order-xyz-123&discount=20%25"
if let url = URL(string: urlString),
let components = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: true) {
print("Scheme: \(components.scheme ?? "N/A")")
print("Host: \(components.host ?? "N/A")")
print("Path: \(components.path ?? "N/A")")
if let queryItems = components.queryItems {
for item in queryItems {
print("Query: \(item.name) = \(item.value ?? "N/A")")
}
}
}
处理 Universal Links (通用链接)
URL Scheme 有一个缺点:当用户设备上没有安装你的应用时,点击链接会弹出一个错误提示,体验很差。
Universal Links (通用链接) 是 Apple 推荐的替代方案,它有巨大优势:
- 无弹窗:如果应用未安装,链接会在 Safari 中正常打开。
- 唯一性:不会像 URL Scheme 那样可能被其他应用“劫持”。
- 安全性:通过关联你的域名和 App ID,确保只有你的应用能处理该链接。
虽然 Universal Links 不使用 scheme:// 格式,但它也支持在路径中传递参数,其解析方式与通过 URLComponents 解析普通网页 URL 完全相同。
| 特性 | URL Scheme | Universal Links |
|---|---|---|
| 格式 | myapp://... |
https://yourdomain.com/... |
| 主要用途 | 应用间通信、深度链接 | 深度链接 |
| 应用未安装时 | 弹出错误提示 | 在 Safari 中打开网页 |
| 安全性 | 可能被其他应用注册相同的 Scheme | 高,与域名绑定,唯一性保证 |
| 配置 | 在 Info.plist 中配置 |
在 Apple Developer 后台和 Web 服务器上配置 |
| 适用场景 | 需要从其他 App、短信、邮件等地方快速拉起你的 App | 官方的、最佳的深度链接方案 |
对于大多数现代应用,Universal Links 是首选的深度链接方案,但在某些特定场景下,例如从一个已知的、可信的 App(如你的公司另一款 App)中跳转,或者需要实现“返回应用”的功能时,URL Scheme 仍然非常有用,理解如何处理其参数是掌握 iOS 应用间通信的基础。