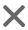
- 请求参数是什么?
- 两种主要的请求参数传递方式:
- 查询字符串参数 (Query String Parameters)
- 请求体参数 (Request Body Parameters)
- 如何使用
fetch发送这两种参数。 - 如何使用
axios发送这两种参数。 - 两种方式的区别与选择。
- 一个完整的示例。
请求参数是什么?
请求参数就是客户端(浏览器)发送给服务器,用于告知服务器“我想要什么”或“这是我的数据”的信息。
(图片来源网络,侵删)
当你搜索商品时,你在搜索框输入的“手机”就是一个参数,服务器会根据这个参数返回相关的商品列表。
两种主要的请求参数传递方式
在 HTTP 请求中,最常用的传递参数的方式有两种,它们分别对应不同的 HTTP 方法。
查询字符串参数
- 位置:放在 URL 的 之后。
- 格式:
key1=value1&key2=value2。 - HTTP 方法:通常与
GET请求一起使用,因为GET请求旨在获取数据,而不是修改数据,所以参数放在 URL 中更直观,也方便书签和分享。 - 特点:
- 参数会直接暴露在 URL 中,不适合传递敏感信息(如密码)。
- URL 长度是有限制的(不同浏览器和服务器限制不同,通常为 2KB-8KB),不适合传输大量数据。
- 主要用于筛选、排序、分页等。
示例 URL:
https://example.com/api/users?page=1&limit=10&sort=asc
page=1: 获取第 1 页的数据。limit=10: 每页显示 10 条。sort=asc: 按“升序”排列。
请求体参数
- 位置:放在 HTTP 请求的
body部分。 - HTTP 方法:通常与
POST,PUT,PATCH等方法一起使用,这些方法用于“创建”、“更新”或“部分更新”资源,需要向服务器提交数据。 - 数据格式:请求体中的数据可以是多种格式,最常见的是:
- JSON: 最现代、最通用的格式,推荐使用。
- form data: 用于传统的表单提交。
- 特点:
- 参数不会出现在 URL 中,相对安全。
- 可以传输大量数据,理论上只受服务器限制。
- 主要用于提交表单、创建/更新资源。
示例 (假设是创建一个新用户):
请求 URL 可能是 https://example.com/api/users。
请求体是:
(图片来源网络,侵删)
{
"username": "john_doe",
"email": "john.doe@example.com",
"password": "a-very-secure-password"
}
如何使用 fetch 发送参数
fetch 是浏览器内置的现代 API,使用 Promise 处理异步请求。
A. 使用 fetch 发送查询字符串参数
我们需要手动拼接 URL。
// 1. 定义参数
const params = {
page: 2,
limit: 5,
category: 'books'
};
// 2. 将参数对象转换为查询字符串
// 使用 URLSearchParams 是最简单、最安全的方式(会自动处理编码)
const queryString = new URLSearchParams(params).toString(); // "page=2&limit=5&category=books"
// 3. 构建完整的 URL
const url = `https://example.com/api/products?${queryString}`;
// 4. 发送 GET 请求
fetch(url)
.then(response => {
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error('Network response was not ok');
}
return response.json(); // 解析 JSON 响应
})
.then(data => {
console.log('获取到的数据:', data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('请求出错:', error);
});
B. 使用 fetch 发送请求体参数
我们需要在 fetch 的第二个参数(一个配置对象)中设置 method 和 body。
// 1. 定义要发送的数据(通常是 JSON 对象)
const userData = {
name: 'Alice',
email: 'alice@example.com',
age: 30
};
// 2. 发送 POST 请求
fetch('https://example.com/api/users', {
method: 'POST', // 指定 HTTP 方法
headers: {
// 告诉服务器我们发送的是 JSON 格式的数据
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
// 将 JavaScript 对象转换为 JSON 字符串作为请求体
body: JSON.stringify(userData),
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log('服务器响应:', data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('请求出错:', error);
});
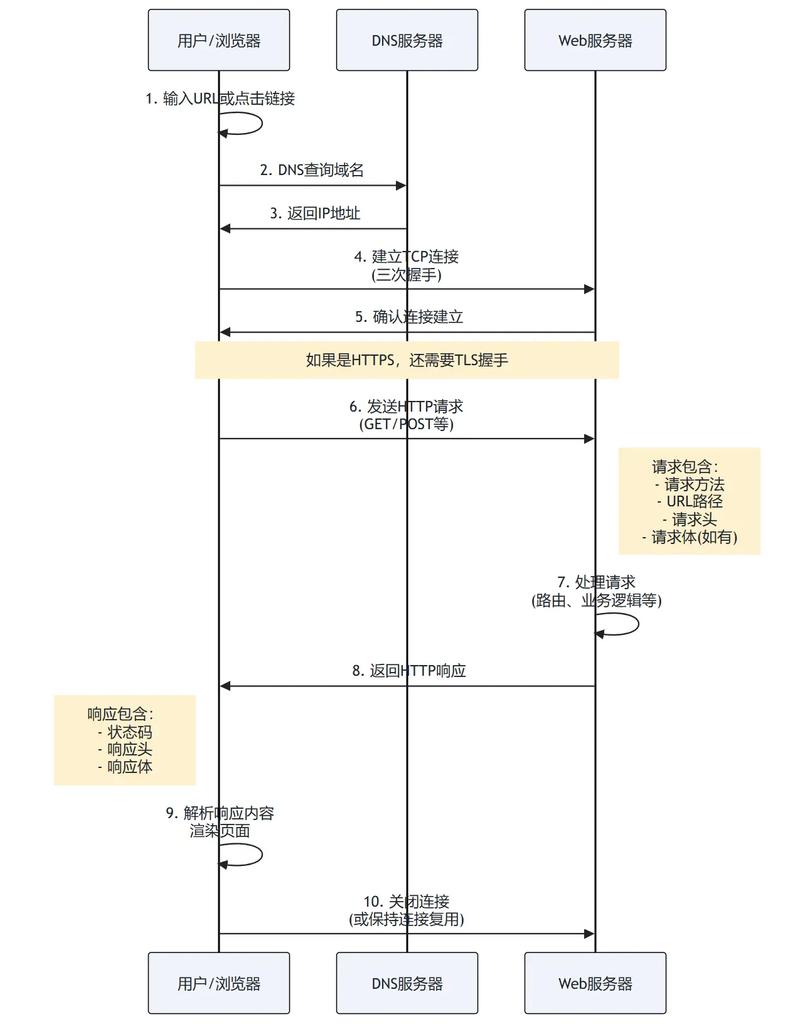
如何使用 axios 发送参数
axios 是一个非常流行的第三方库,它封装了 fetch,提供了更简洁的 API 和一些便利功能(如自动 JSON 转换、拦截器等),首先需要安装:npm install axios 或使用 CDN。
(图片来源网络,侵删)
A. 使用 axios 发送查询字符串参数
axios 会自动将 params 对象转换为查询字符串。
import axios from 'axios'; // 或通过 script 标签引入
// 1. 定义参数
const params = {
page: 2,
limit: 5,
category: 'books'
};
// 2. 发送 GET 请求,axios 会自动处理 params
axios.get('https://example.com/api/products', {
params: params // axios 会自动将其转换为 ?page=2&limit=5&category=books
})
.then(response => {
console.log('获取到的数据:', response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('请求出错:', error);
});
B. 使用 axios 发送请求体参数
我们只需要在配置对象中提供 data 属性即可。
import axios from 'axios';
// 1. 定义要发送的数据
const userData = {
name: 'Bob',
email: 'bob@example.com',
age: 25
};
// 2. 发送 POST 请求
axios.post('https://example.com/api/users', userData)
.then(response => {
console.log('服务器响应:', response.data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('请求出错:', error);
});
注意:
axios会自动将 JavaScript 对象序列化为 JSON 字符串,并自动设置Content-Type: application/json头,这使得它比fetch更为方便。
两种方式的区别与选择
| 特性 | 查询字符串参数 | 请求体参数 |
|---|---|---|
| 位置 | URL 的 之后 | HTTP 请求的 body 部分 |
| HTTP 方法 | 主要 GET |
主要 POST, PUT, PATCH |
| 可见性 | 公开,会显示在地址栏 | 私有,不会显示在地址栏 |
| 数据量 | 有限,受 URL 长度限制 | 较大,只受服务器限制 |
| 安全性 | 低,不适合传敏感信息 | 较高,适合传敏感信息 |
| 主要用途 | 获取/筛选数据 (分页、排序、搜索) | 提交/创建/更新数据 (表单、上传) |
如何选择?
- 获取数据时:使用
GET请求和查询字符串参数。GET /api/users?role=admin。 - 提交数据时:使用
POST请求和请求体参数。POST /api/users,在 body 中包含新用户的信息。 - 更新数据时:使用
PUT或PATCH请求和请求体参数。PUT /api/users/123,在 body 中包含更新后的完整用户信息。
一个完整的示例
下面是一个简单的网页,它同时展示了如何通过查询字符串获取数据和通过请求体提交数据。
HTML (index.html)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">JS 请求参数示例</title>
<style>
body { font-family: sans-serif; margin: 2em; }
input, button { padding: 8px; margin: 5px; }
#result { margin-top: 20px; border: 1px solid #ccc; padding: 10px; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JavaScript 请求参数示例</h1>
<div>
<h2>1. 获取数据 (GET 请求)</h2>
<button id="getDataBtn">获取用户列表 (带参数)</button>
<div id="getDataResult"></div>
</div>
<hr>
<div>
<h2>2. 提交数据 (POST 请求)</h2>
<input type="text" id="userName" placeholder="用户名">
<input type="email" id="userEmail" placeholder="邮箱">
<button id="postDataBtn">创建新用户</button>
<div id="postDataResult"></div>
</div>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript (app.js)
// --- 获取数据示例 (GET with Query String) ---
const getDataBtn = document.getElementById('getDataBtn');
const getDataResult = document.getElementById('getDataResult');
getDataBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
getDataResult.textContent = '正在获取数据...';
// 模拟的 API 端点,实际开发中替换为真实的 URL
const apiUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users';
// 定义查询参数
const queryParams = {
_limit: 3 // 只获取前3个用户
};
// 使用 axios 发送请求
axios.get(apiUrl, { params: queryParams })
.then(response => {
// response.data 是一个用户数组
const users = response.data;
let html = '<ul>';
users.forEach(user => {
html += `<li><strong>${user.name}</strong> (${user.email})</li>`;
});
html += '</ul>';
getDataResult.innerHTML = html;
})
.catch(error => {
getDataResult.innerHTML = `<p style="color: red;">请求失败: ${error.message}</p>`;
});
});
// --- 提交数据示例 (POST with Request Body) ---
const postDataBtn = document.getElementById('postDataBtn');
const postDataResult = document.getElementById('postDataResult');
const userNameInput = document.getElementById('userName');
const userEmailInput = document.getElementById('userEmail');
postDataBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
const name = userNameInput.value;
const email = userEmailInput.value;
if (!name || !email) {
postDataResult.innerHTML = '<p style="color: orange;">请填写用户名和邮箱</p>';
return;
}
postDataResult.textContent = '正在创建用户...';
// 模拟的 API 端点
const apiUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users';
// 准备要发送的数据
const newUser = {
name: name,
email: email,
// jsonplaceholder.typicode.com 会忽略这个字段,但我们可以加上
username: name.toLowerCase().replace(' ', '_')
};
// 使用 axios 发送 POST 请求
axios.post(apiUrl, newUser)
.then(response => {
const createdUser = response.data;
postDataResult.innerHTML = `
<p style="color: green;">用户创建成功!</p>
<p><strong>ID:</strong> ${createdUser.id}</p>
<p><strong>姓名:</strong> ${createdUser.name}</p>
<p><strong>邮箱:</strong> ${createdUser.email}</p>
`;
// 清空输入框
userNameInput.value = '';
userEmailInput.value = '';
})
.catch(error => {
postDataResult.innerHTML = `<p style="color: red;">创建失败: ${error.message}</p>`;
});
});
这个例子清晰地展示了 axios 如何优雅地处理 params 和 data,使代码非常简洁易读。